Table Of Content
The topic here is traditional theory which does not change quickly as typical IT topics do. Any updates should be easily implemented, but very few would be expected. The book contains the Table of Contents and lists Key Terms for every Chapter. However, it will be better to include Index with corresponding page numbers and/or hyperlinks.
model
The university offers bachelor of science, master of science, professional master’s, and Ph.D. degrees—as well as certificates for in-demand STEM fields and other areas of innovation. Talented students from around the world choose to study at Illinois Tech because of the access to real-world opportunities, renowned academic programs, high value, and career prospects of graduates. Work together to design, model and document the database schema of your app. Visualize your database schema and gain a birds-eye view of how different models fits together. Create a living document of your database schema that helps when architecting new features or onboarding new team members. BRANCH_CODE of STUDENT can only take the values which are present in BRANCH_CODE of BRANCH which is called referential integrity constraint.
Base and derived relations

The process of putting this diagram together can help us straighten out the relationships and identify important insights or redundant attributes as we go. What types of entities do we need to create tables for (customers, orders, products, courses, website-clicks, data downloads, etc)? As with anything to do with taking advantage of data, to make our work most effective we need to think about what the use cases are and what our users are looking for. If we tried to store the key for the product on the brand table, we’d have to have a record for each product — making the separation of the data pointless and creating unnecessary redundancy in our database.
Anomalies in the Relational Model
For example, a table of customers might have columns for name, email, phone number, and address. Each row in the table would have the information for one customer. They’ve been used to build a wide variety of different applications, and continue working efficiently even with very large amounts of data.
Relational Database Design Process
Guidelines (usually in terms of what not to do instead of what to do) are provided in making these design decision, but the choices ultimately rest on the you - the designer. It accuracy is very good and it admits is covers most topics in databases.It's a great intro to databases book. For example, both chapters 10 and 11 begin by introducing the concept of functional dependency. I would have expected the concept to be fully defined and explained in one chapter or the other, not both, or at the very least make it clear that the concept is broken up into multiple chapters. Some topics seemed to appear out of the blue in the middle of some chapters without warning. Chapters were inconsistent in terms of their length and the depth and care with which they treated a subject.
Practical Examples: Implementing Data Models in DBMS
The column teacherID in the child table Classes is known as the foreign key. A foreign key of a child table is a primary key of a parent table, used to reference the parent table. Part of the programming within a RDBMS is accomplished using stored procedures (SPs). Often procedures can be used to greatly reduce the amount of information transferred within and outside of a system.
Fauna Adds Groundbreaking New Database Language and Seamless Developer Experience to Enterprise Proven ... - Business Wire
Fauna Adds Groundbreaking New Database Language and Seamless Developer Experience to Enterprise Proven ....
Posted: Tue, 22 Aug 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Advantages of the Entity-Attribute-Value
Due to hardware constraints, early relational databases were still prohibitively slow, and it took some time before the technology became widespread. But by the mid-1980s, Codd’s relational model had been implemented in a number of commercial database management products from both IBM and its competitors. These vendors also followed IBM’s lead by developing and implementing their own dialects of SQL.
Index can be defined on a single column, a set of columns (called concatenated index), or part of a column (e.g., first 10 characters of a VARCHAR(100)) (called partial index) . For example, if you often search for a customer using either customerName or phoneNumber, you could speed up the search by building an index on column customerName, as well as phoneNumber. Choose one column (or a few columns) as the so-called primary key, which uniquely identify the each of the rows.
Step 3: Create a list of entities and a list of attributes
The text handles this issue as well as any, however, and doesn't delve into most of the areas where implementations differ the most. Adding glossary and index, however, would help readers locate important concepts more easily. Remember that continuous learning is key in this ever-evolving tech world! Use online resources such as tutorials, webinars or even YouTube videos to stay ahead in the game. Scale AI workloads for all your data, anywhere, with IBM watsonx.data, a fit-for-purpose data store built on an open data lakehouse architecture.
Relations can be modified using the insert, delete, and update operators. New tuples can supply explicit values or be derived from a query. When you take online courses about database design, you will learn how to come up with the full design of the database. This work will include each of the necessary elements, including designing and implementing the database schema, tables, indexes, columns, and fields.
The first thing to do is to read the requirements document carefully, making note of the things which might become entities in our database, and the possible relationships between them. The first thing to think about when creating a database is what we want it for. Different requirements will lead to different information structures, relationships, designs and implementations.
This means choosing the right data types, setting up relationships properly, and ensuring everything correlates effectively. In our case, an arbitrary ‘product_id’ has been assigned to each record. Which to use depends on the nature of your data — what is important is that every table has a primary key, it must be unique and it cannot be NULL.
Learn about IBM Db2, the cloud-native database built to power low-latency transactions and real-time analytics at scale. Here we are storing the client_name, address and industry attributes, alongside a unique client_id. Bear in mind that a real requirements document will likely be longer and more complex than this, but this one will give us the information we need to build our example database. The school has clients, each of whom may offer multiple courses via the school.
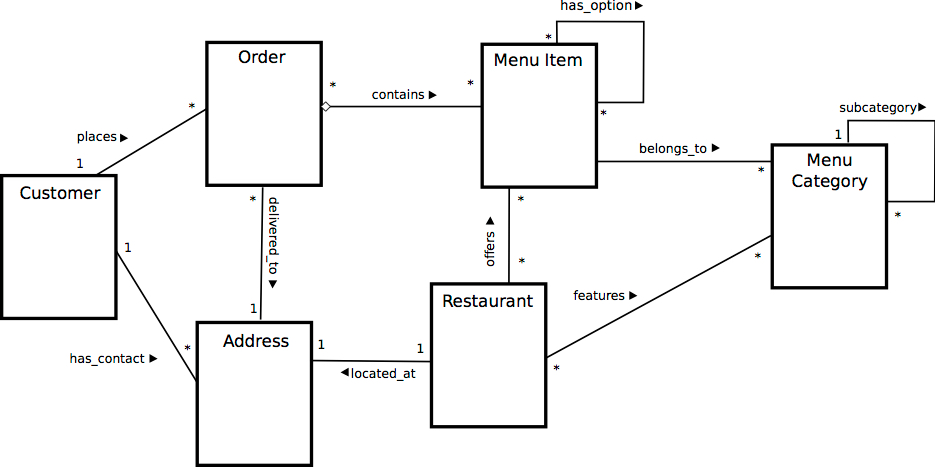
The key factor here is the effective correlation and storage of data elements – this is what makes or breaks a well-designed database system. While relational databases have historically been viewed as a more rigid and inflexible data storage option, advances in technology and DBaaS options are changing that perception. While there is still more overhead to develop schemas compared to NoSQL database offerings, relational databases are becoming more flexible as they migrate to cloud environments. A very useful intermediate step between getting the requirements and implementing our database in SQL is creating an Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD). This is, as you might anticipate, a diagram which maps the relationships between the entities that we will build into our database.
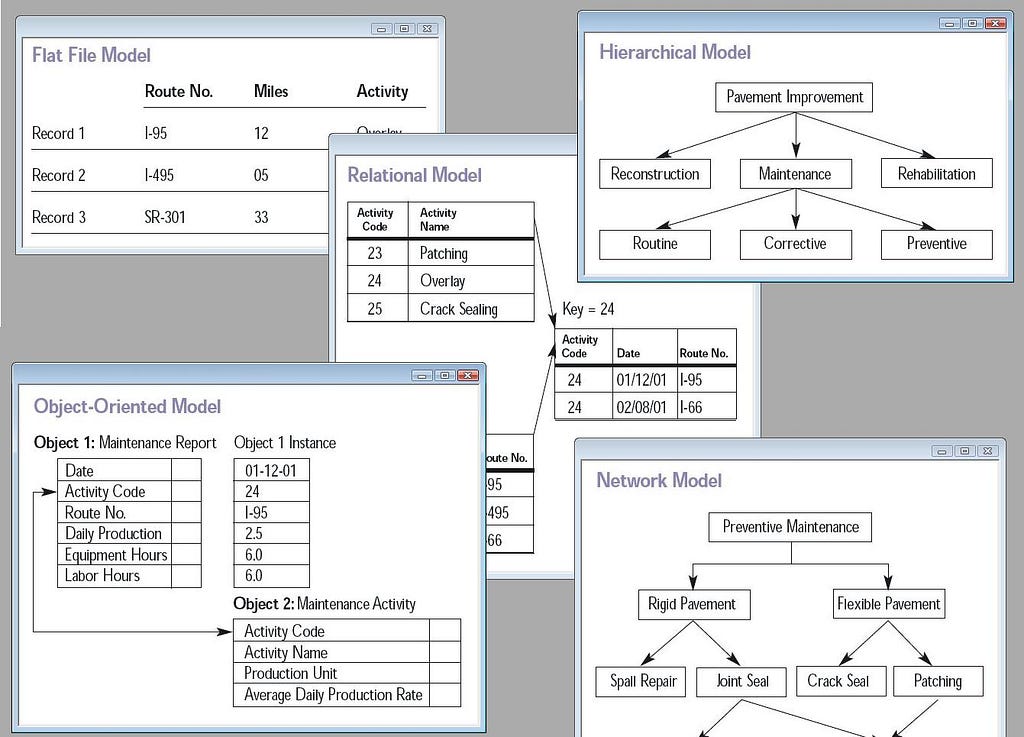
Before relational databases, companies used a hierarchical database system with a tree-like structure for the data tables. These early database management systems (DBMS) enabled users to organize large quantities of data. However, they were complex, often proprietary to a particular application, and limited in the ways in which they could uncover within the data. This is a design pattern where a combination of two or more columns is used to uniquely identify each row in a table, instead of having a single column as the primary key. The relational databases require defining a primary key for each table, which is a column or a set of columns that can distinguish each row from others.
Another example of domain describes the possible values for the field "CoinFace" as ("Heads","Tails"). So, the field "CoinFace" will not accept input values like (0,1) or (H,T). The book is consistent in terms of terminology and organization of the concepts in every chapter. I had to zoom very large and they were still sometimes very hard to read.
No comments:
Post a Comment